 ## About
In 2015, juCi++ was one of the first IDEs to utilize libclang for improved C/C++ tooling. The
integrated C/C++ support has since then improved steadily, and support for other languages has been
made possible through the language server protocol. The main goals of juCi++ is effective resource
usage, stability, and ease of use. Instead of relying on 3rd party addons, features expected in an
IDE is instead integrated directly into juCi++.
For effective development, juCi++ is primarily written for Unix/Linux systems. However, Windows
users can use juCi++ through POSIX compatibility layers such as MSYS2.
## Installation
See [installation guide](docs/install.md).
## Features
- Platform independent
- Fast, responsive and stable (written extensively using C++11/14 features)
- Syntax highlighting for more than 100 different file types
- Warnings and errors on the fly
- Fix-its, as well as C/C++ standard header include suggestions
- Integrated Clang-Tidy checks can be enabled in preferences
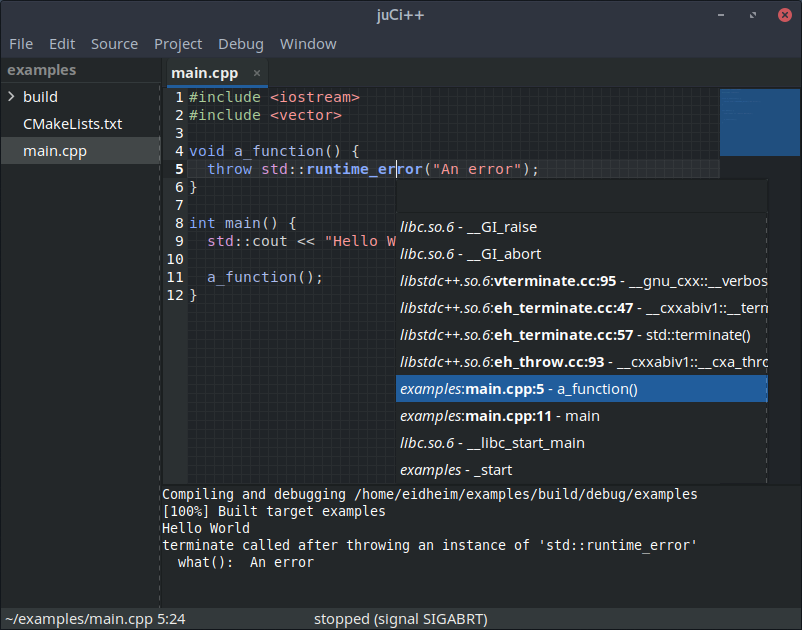
- Debug integration, both local and remote, through lldb
- Supports the following C/C++ build systems directly (other build systems need manually generated
compilation databases):
- CMake
- Meson
- Fast autocompletion
- Tooltips showing type information and documentation
- Rename refactoring across files
- Highlighting of similar types
- Automated documentation search for C/C++ identifiers
- Go to declaration, implementation, methods and usages
- OpenCL and CUDA files are supported and parsed as C++
- Non-C/C++ files are supported through the Language Server Protocol, which is enabled if an
`[language identifier]-language-server` executable is found. This executable can be a symbolic
link to one of your installed language server binaries.
- For additional instructions, see: [setup of tested language servers](docs/language_servers.md)
- Non-C/C++ projects are also supported, such as JavaScript, Python, Rust, and Go projects
- Git support through libgit2
- Find symbol through Ctags ([Universal Ctags](https://github.com/universal-ctags/ctags) is
recommended)
- Spell checking depending on file context
- Run shell commands within juCi++
- ANSI colors are supported. Enable for instance by setting the environment variables
`CLICOLOR=1 CLICOLOR_FORCE=1` before starting juCi++. Colored diagnostics from clang is enabled
through the flag `-fcolor-diagnostics`, and gcc uses the flag `-fdiagnostics-color`.
- Regex search and replace
- Smart paste, keys and indentation
- Extend/shrink selection
- Multiple cursors
- Snippets can be added in ~/.juci/snippets.json using the
[TextMate snippet syntax](https://macromates.com/manual/en/snippets). The language ids used in the
regexes can be found here:
https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/gtksourceview/tree/master/data/language-specs.
- Auto-indentation through [clang-format](http://clang.llvm.org/docs/ClangFormat.html) or
[Prettier](https://github.com/prettier/prettier) if installed
- Source minimap
- Split view
- Zen mode
- Full UTF-8 support
- Wayland supported with GTK+ 3.20 or newer
See
[enhancements](https://gitlab.com/cppit/jucipp/issues?scope=all&state=opened&label_name[]=enhancement)
for planned features.
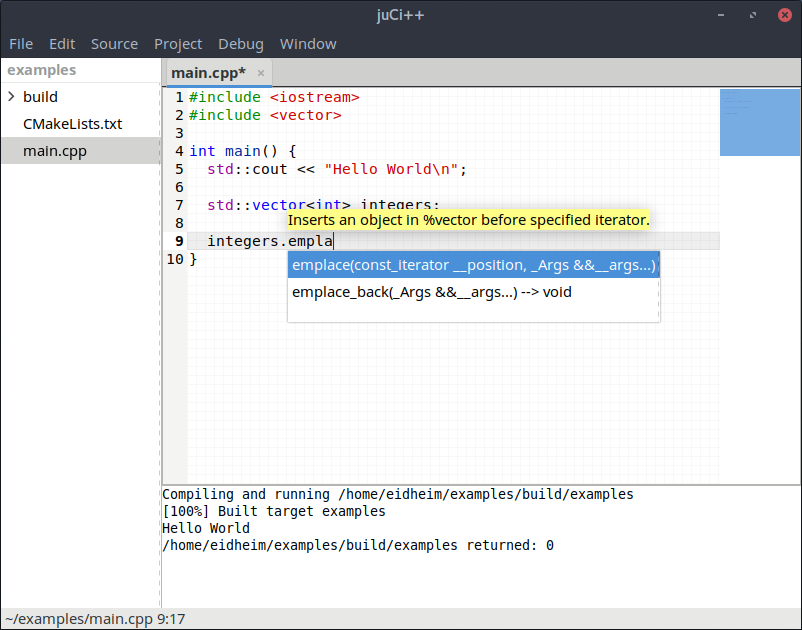
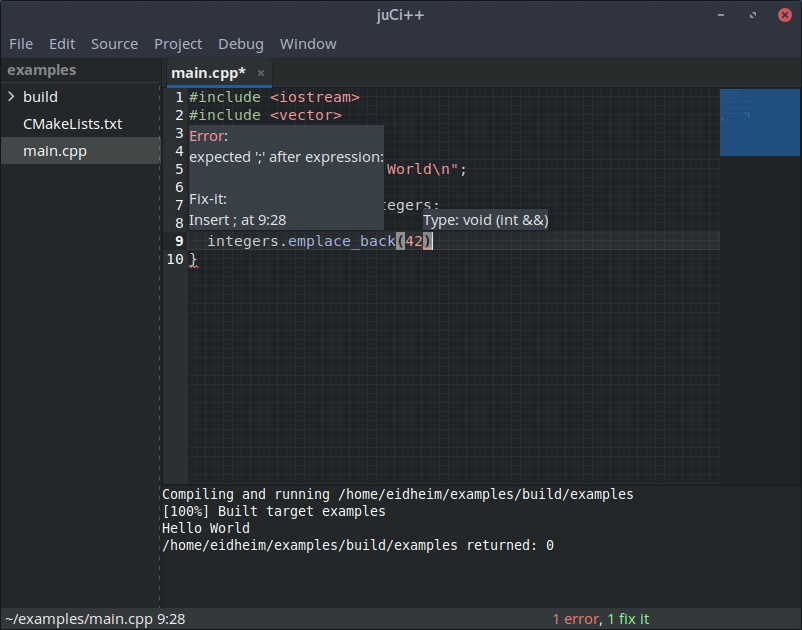
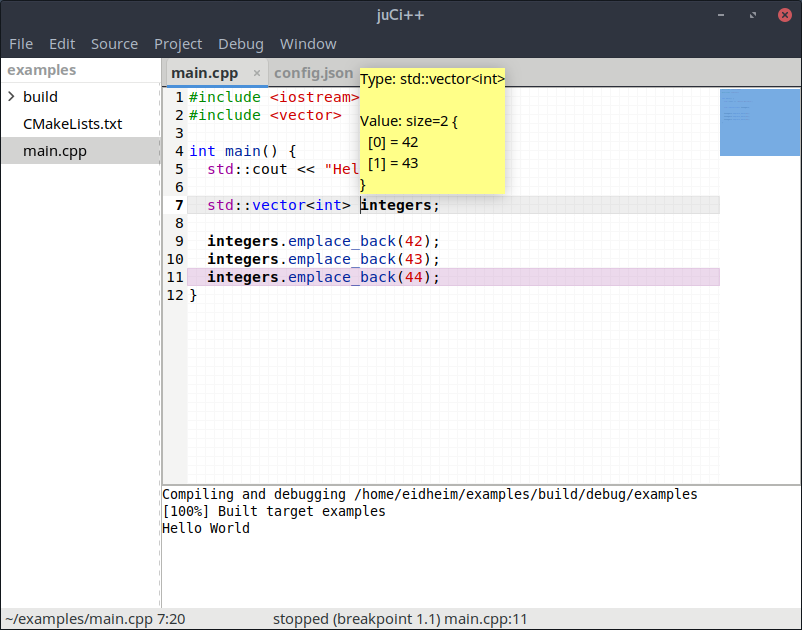
## Screenshots
## Custom styling
See [custom styling](docs/custom_styling.md).
## Dependencies
- boost-filesystem
- boost-serialization
- gtkmm-3.0
- gtksourceviewmm-3.0
- aspell
- libclang
- lldb
- libgit2
- [libclangmm](http://gitlab.com/cppit/libclangmm/) (downloaded directly with git --recursive, no
need to install)
- [tiny-process-library](http://gitlab.com/eidheim/tiny-process-library/) (downloaded directly with
git --recursive, no need to install)
## Documentation
See [how to build the API doc](docs/api.md).
## About
In 2015, juCi++ was one of the first IDEs to utilize libclang for improved C/C++ tooling. The
integrated C/C++ support has since then improved steadily, and support for other languages has been
made possible through the language server protocol. The main goals of juCi++ is effective resource
usage, stability, and ease of use. Instead of relying on 3rd party addons, features expected in an
IDE is instead integrated directly into juCi++.
For effective development, juCi++ is primarily written for Unix/Linux systems. However, Windows
users can use juCi++ through POSIX compatibility layers such as MSYS2.
## Installation
See [installation guide](docs/install.md).
## Features
- Platform independent
- Fast, responsive and stable (written extensively using C++11/14 features)
- Syntax highlighting for more than 100 different file types
- Warnings and errors on the fly
- Fix-its, as well as C/C++ standard header include suggestions
- Integrated Clang-Tidy checks can be enabled in preferences
- Debug integration, both local and remote, through lldb
- Supports the following C/C++ build systems directly (other build systems need manually generated
compilation databases):
- CMake
- Meson
- Fast autocompletion
- Tooltips showing type information and documentation
- Rename refactoring across files
- Highlighting of similar types
- Automated documentation search for C/C++ identifiers
- Go to declaration, implementation, methods and usages
- OpenCL and CUDA files are supported and parsed as C++
- Non-C/C++ files are supported through the Language Server Protocol, which is enabled if an
`[language identifier]-language-server` executable is found. This executable can be a symbolic
link to one of your installed language server binaries.
- For additional instructions, see: [setup of tested language servers](docs/language_servers.md)
- Non-C/C++ projects are also supported, such as JavaScript, Python, Rust, and Go projects
- Git support through libgit2
- Find symbol through Ctags ([Universal Ctags](https://github.com/universal-ctags/ctags) is
recommended)
- Spell checking depending on file context
- Run shell commands within juCi++
- ANSI colors are supported. Enable for instance by setting the environment variables
`CLICOLOR=1 CLICOLOR_FORCE=1` before starting juCi++. Colored diagnostics from clang is enabled
through the flag `-fcolor-diagnostics`, and gcc uses the flag `-fdiagnostics-color`.
- Regex search and replace
- Smart paste, keys and indentation
- Extend/shrink selection
- Multiple cursors
- Snippets can be added in ~/.juci/snippets.json using the
[TextMate snippet syntax](https://macromates.com/manual/en/snippets). The language ids used in the
regexes can be found here:
https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/gtksourceview/tree/master/data/language-specs.
- Auto-indentation through [clang-format](http://clang.llvm.org/docs/ClangFormat.html) or
[Prettier](https://github.com/prettier/prettier) if installed
- Source minimap
- Split view
- Zen mode
- Full UTF-8 support
- Wayland supported with GTK+ 3.20 or newer
See
[enhancements](https://gitlab.com/cppit/jucipp/issues?scope=all&state=opened&label_name[]=enhancement)
for planned features.
## Screenshots
## Custom styling
See [custom styling](docs/custom_styling.md).
## Dependencies
- boost-filesystem
- boost-serialization
- gtkmm-3.0
- gtksourceviewmm-3.0
- aspell
- libclang
- lldb
- libgit2
- [libclangmm](http://gitlab.com/cppit/libclangmm/) (downloaded directly with git --recursive, no
need to install)
- [tiny-process-library](http://gitlab.com/eidheim/tiny-process-library/) (downloaded directly with
git --recursive, no need to install)
## Documentation
See [how to build the API doc](docs/api.md).
 ## About
In 2015, juCi++ was one of the first IDEs to utilize libclang for improved C/C++ tooling. The
integrated C/C++ support has since then improved steadily, and support for other languages has been
made possible through the language server protocol. The main goals of juCi++ is effective resource
usage, stability, and ease of use. Instead of relying on 3rd party addons, features expected in an
IDE is instead integrated directly into juCi++.
For effective development, juCi++ is primarily written for Unix/Linux systems. However, Windows
users can use juCi++ through POSIX compatibility layers such as MSYS2.
## Installation
See [installation guide](docs/install.md).
## Features
- Platform independent
- Fast, responsive and stable (written extensively using C++11/14 features)
- Syntax highlighting for more than 100 different file types
- Warnings and errors on the fly
- Fix-its, as well as C/C++ standard header include suggestions
- Integrated Clang-Tidy checks can be enabled in preferences
- Debug integration, both local and remote, through lldb
- Supports the following C/C++ build systems directly (other build systems need manually generated
compilation databases):
- CMake
- Meson
- Fast autocompletion
- Tooltips showing type information and documentation
- Rename refactoring across files
- Highlighting of similar types
- Automated documentation search for C/C++ identifiers
- Go to declaration, implementation, methods and usages
- OpenCL and CUDA files are supported and parsed as C++
- Non-C/C++ files are supported through the Language Server Protocol, which is enabled if an
`[language identifier]-language-server` executable is found. This executable can be a symbolic
link to one of your installed language server binaries.
- For additional instructions, see: [setup of tested language servers](docs/language_servers.md)
- Non-C/C++ projects are also supported, such as JavaScript, Python, Rust, and Go projects
- Git support through libgit2
- Find symbol through Ctags ([Universal Ctags](https://github.com/universal-ctags/ctags) is
recommended)
- Spell checking depending on file context
- Run shell commands within juCi++
- ANSI colors are supported. Enable for instance by setting the environment variables
`CLICOLOR=1 CLICOLOR_FORCE=1` before starting juCi++. Colored diagnostics from clang is enabled
through the flag `-fcolor-diagnostics`, and gcc uses the flag `-fdiagnostics-color`.
- Regex search and replace
- Smart paste, keys and indentation
- Extend/shrink selection
- Multiple cursors
- Snippets can be added in ~/.juci/snippets.json using the
[TextMate snippet syntax](https://macromates.com/manual/en/snippets). The language ids used in the
regexes can be found here:
https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/gtksourceview/tree/master/data/language-specs.
- Auto-indentation through [clang-format](http://clang.llvm.org/docs/ClangFormat.html) or
[Prettier](https://github.com/prettier/prettier) if installed
- Source minimap
- Split view
- Zen mode
- Full UTF-8 support
- Wayland supported with GTK+ 3.20 or newer
See
[enhancements](https://gitlab.com/cppit/jucipp/issues?scope=all&state=opened&label_name[]=enhancement)
for planned features.
## Screenshots
## About
In 2015, juCi++ was one of the first IDEs to utilize libclang for improved C/C++ tooling. The
integrated C/C++ support has since then improved steadily, and support for other languages has been
made possible through the language server protocol. The main goals of juCi++ is effective resource
usage, stability, and ease of use. Instead of relying on 3rd party addons, features expected in an
IDE is instead integrated directly into juCi++.
For effective development, juCi++ is primarily written for Unix/Linux systems. However, Windows
users can use juCi++ through POSIX compatibility layers such as MSYS2.
## Installation
See [installation guide](docs/install.md).
## Features
- Platform independent
- Fast, responsive and stable (written extensively using C++11/14 features)
- Syntax highlighting for more than 100 different file types
- Warnings and errors on the fly
- Fix-its, as well as C/C++ standard header include suggestions
- Integrated Clang-Tidy checks can be enabled in preferences
- Debug integration, both local and remote, through lldb
- Supports the following C/C++ build systems directly (other build systems need manually generated
compilation databases):
- CMake
- Meson
- Fast autocompletion
- Tooltips showing type information and documentation
- Rename refactoring across files
- Highlighting of similar types
- Automated documentation search for C/C++ identifiers
- Go to declaration, implementation, methods and usages
- OpenCL and CUDA files are supported and parsed as C++
- Non-C/C++ files are supported through the Language Server Protocol, which is enabled if an
`[language identifier]-language-server` executable is found. This executable can be a symbolic
link to one of your installed language server binaries.
- For additional instructions, see: [setup of tested language servers](docs/language_servers.md)
- Non-C/C++ projects are also supported, such as JavaScript, Python, Rust, and Go projects
- Git support through libgit2
- Find symbol through Ctags ([Universal Ctags](https://github.com/universal-ctags/ctags) is
recommended)
- Spell checking depending on file context
- Run shell commands within juCi++
- ANSI colors are supported. Enable for instance by setting the environment variables
`CLICOLOR=1 CLICOLOR_FORCE=1` before starting juCi++. Colored diagnostics from clang is enabled
through the flag `-fcolor-diagnostics`, and gcc uses the flag `-fdiagnostics-color`.
- Regex search and replace
- Smart paste, keys and indentation
- Extend/shrink selection
- Multiple cursors
- Snippets can be added in ~/.juci/snippets.json using the
[TextMate snippet syntax](https://macromates.com/manual/en/snippets). The language ids used in the
regexes can be found here:
https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/gtksourceview/tree/master/data/language-specs.
- Auto-indentation through [clang-format](http://clang.llvm.org/docs/ClangFormat.html) or
[Prettier](https://github.com/prettier/prettier) if installed
- Source minimap
- Split view
- Zen mode
- Full UTF-8 support
- Wayland supported with GTK+ 3.20 or newer
See
[enhancements](https://gitlab.com/cppit/jucipp/issues?scope=all&state=opened&label_name[]=enhancement)
for planned features.
## Screenshots



